Features
GAgent is Gizwits’s hardware connectivity with the embedded system firmware that can operate in Wi-Fi modules, GPRS modules and PCs etc. Devices access Gizwits IoT Cloud through the GAgent. GAgent provides the communication protocol between cloud and MCU, so that, according to the protocol, developers can realize the communication between MCU and GAgent.
GAgent plays the role of a data interaction bridge, which is of data forwarding between devices and Gizwits IoT Cloud. At present, the Wi-Fi modules that support GAgent ported by Gizwits are High-Flying LPB100/LPB120/LPT120/LPT220, Espressif 8266, Qualcomm 4004, RealTek 8711AM, WinnerMicro TLN13SP01, Ralinwi TinyCon3350-M26 and MXCHIP EMW3162 etc.; the GPRS modules that support GAgent ported by Gizwits are Fibocom G510 and so on.
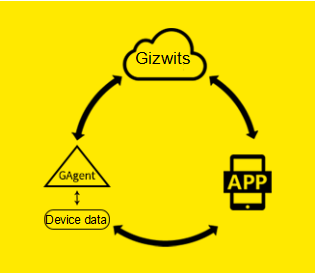
Gizwits IoT Cloud access with GAgent
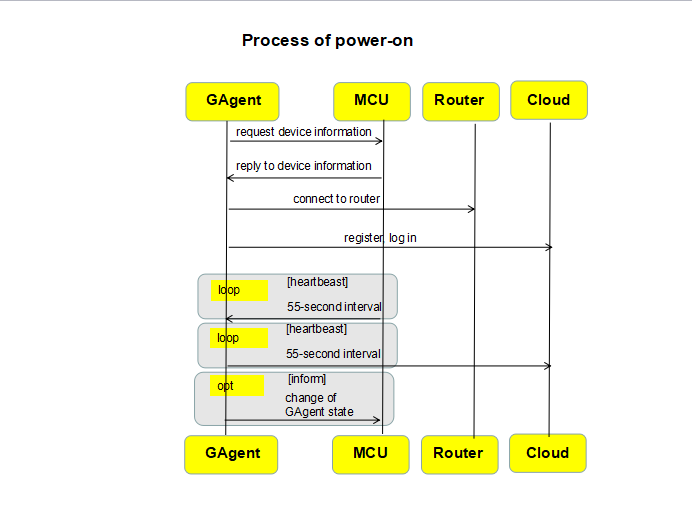
1. Power on device
- GAgent requests device information
- Replies device information to GAgent
- The device works normally and needs to reply to the heartbeat sent by GAgent.
- GAgent notifies MCU of network state changes.
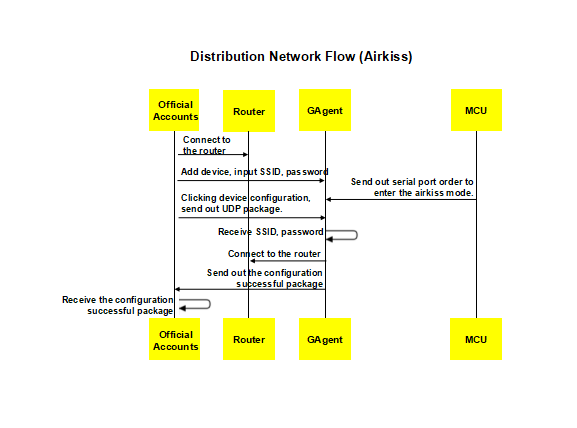
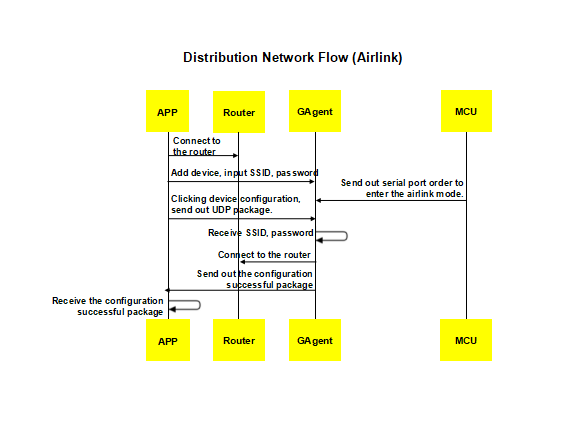
Connect the device to the router. Currently, there are three types of network access configuration, such as AirKiss, AirLink and SoftAP.
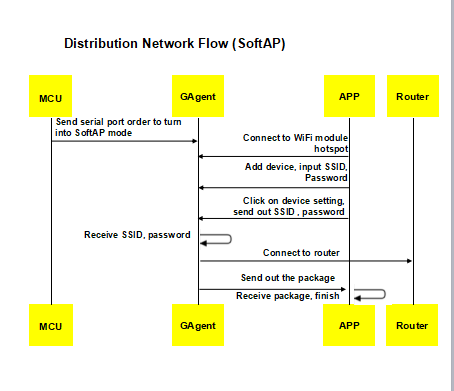
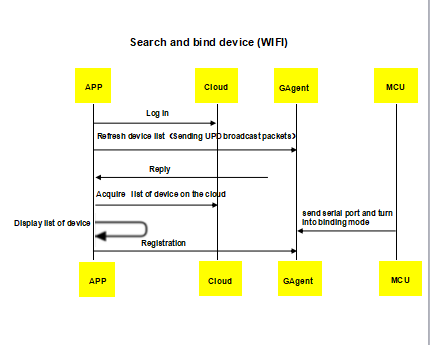
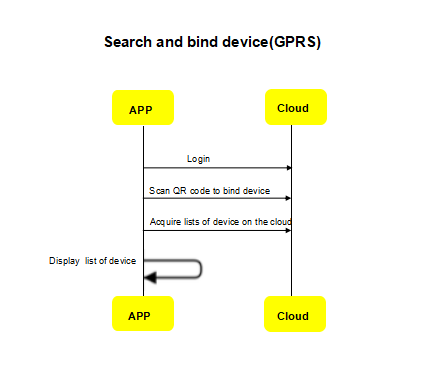
3. Discover and bind device
A device must be bound before it can be controlled. Generally, WLAN is adopted by Wi-Fi modules to discover and bind devices while QR code is used by GPRS modules to scan and bind devices because WLAN is not available.
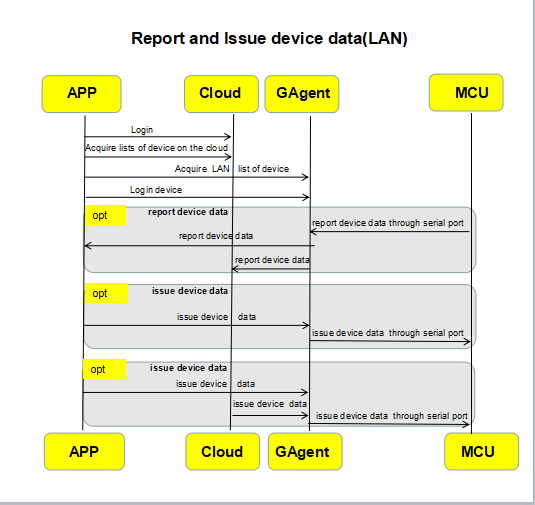
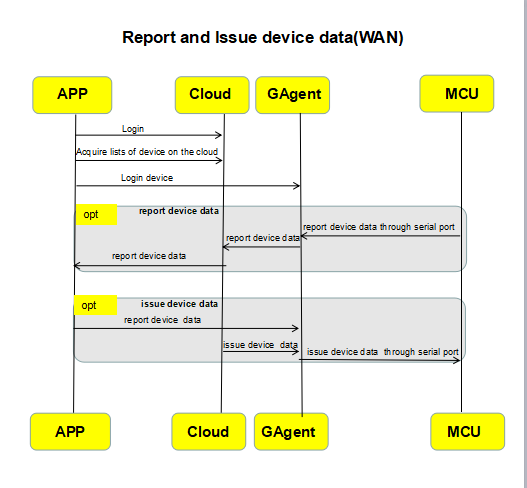
4. Send commands and report device data
Sending commands: Generally refers to controlling devices by App and Gizwits IoT Cloud. The App in the WLAN can choose to send commands through Gizwits IoT Cloud or directly to the GAgent without passing through the cloud.
Reporting device data: Generally refers to actively reporting the current status by device. When the device MCU receives the status changes induced by executing commands, it should immediately report the current status actively, and the sending frequency is not limited. However, if the status changes are due to user operations or environmental changes, the send frequency cannot be more than 6 times per second. It is recommended to report device data on demand. If you have special reporting requirements, please contact Gizwits.
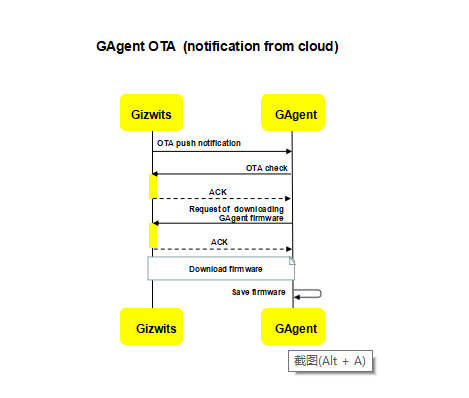
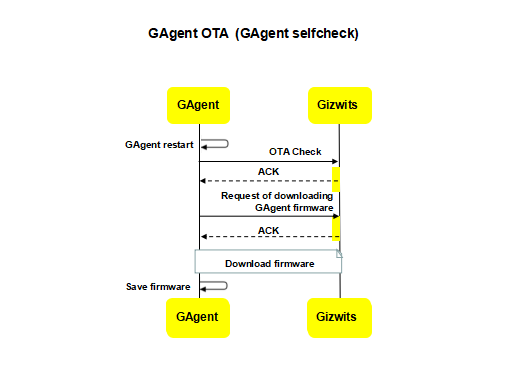
5.GAgent OTA process
GAgent OTA refers to notifying modules of the new version of the GAgent firmware to upgrade after the remote push rule for GAgent is created in Gizwits IoT Cloud. The GAgent OTA has two types of trigger actions: Gizwits IoT Cloud actively notifies modules of the OTA action; the GAgent connects to Gizwits IoT Cloud to check whether the OTA is required.
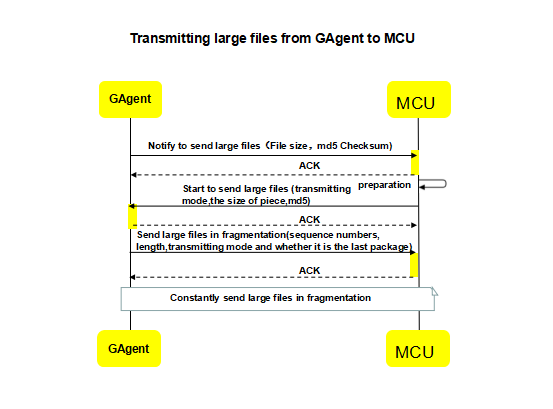
6.MCU OTA process
MCU OTA refers to notifying the MCU of the new version of the MCU firmware to upgrade after the remote push rule for MCU is created in Gizwits IoT Cloud. The MCU OTA process is that GAgen performs the large file transmission to MCU.
7.Large file upload to Gizwits IoT Cloud
When the data collected by the device is too large, the MCU can upload those large files to Gizwits IoT Cloud through GAgent. After uploaded to Gizwits IoT Cloud, they can be obtained through the corresponding APIs. At present, App does not support obtaining large files uploaded by MCU.
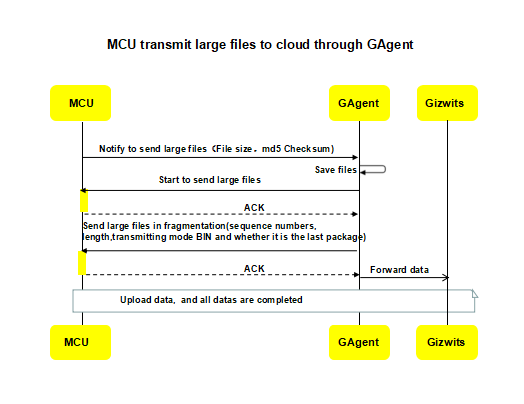
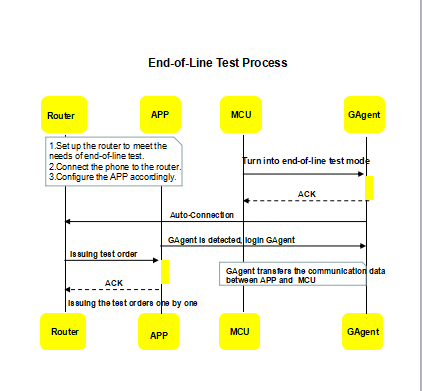
8. End-of-line test
End-of-line test is mainly applied in the process of device production and testing, which is a method of device testing. At present, the End-of-line test is applicable to Wi-Fi modules, but not to GPRS modules.
Key policies of GAgent
1. When to use the restart and reset commands?
When GAgent is unable to connect to Gizwits IoT Cloud for a long time due to some reasons during normal operation, the Wi-Fi module needs to be restarted. The device user can manually restart the device, or send the restart command from MCU to restart the Wi-Fi module. In addition, GAgent has an exception handling policy of restarting itself automatically when an exception occurs.
Reset means to erase the DID, SSID, password and other information saved by GAgent. After sending the reset command, the Wi-Fi module will restart itself. The reset command is mainly used when a device ownership is transferred from A user to B user, B user does not want A user to control the device.
2. How to use the binding expiry?
Gizwits binding expiry policy: When the App and device are in the same LAN and the binding expiry of GAgent is not set, any user with the relevant App can bind the device at any time, which has certain security risks. After the binding expiry is set, the user can only bind the device before the binding expiry, which improves security.
3. Heartbeat policy and offline determination conditions for LAN and WAN
LAN:
Heartbeat between App and GAgent: the heartbeat interval is 4s, when the response timeout happens 3 times, it will cause offline.
WAN:
Heartbeat between App and Gizwits IoT Cloud: the heartbeat interval is 55s, when the response timeout happens 3 times, it will cause offline.
Heartbeat between GAgent and Gizwits IoT Cloud: the heartbeat interval is 55s, when the response timeout happens 3 times, it will cause offline.
4. Network environment requirements
- Some Wi-Fi modules cannot recognize the Chinese SSID. It is recommended to set the router SSID in English.
- AES encryption is recommended for the router.
- Turn off AP isolation
5. Connection policy
- Cache the router hotspot to which the Wi-Fi module most recently connected successfully (no matter whether the external network connection is available)
- Use the current SSID and password to connect to the router. Retry immediately after failure. If the connection is unsuccessful after retrying more than 30s, try to connect to the route hotspot to which the Wi-Fi module most recently connected successfully (assume that the current hotspot is different from the hotspot of last successful connection). If it still fails, try to connect to the current hotspot and the hotspot of last successful connection alternately.
- If it still fails after retrying more than 2 minutes, , restart the module in STA mode and repeat the previous step.
- When it succeeds, update the current SSID/password and the SSID/password of the successful connection.
Note: The current SSID and the SSID of the most recent connection may be the same.
6. Network access configuration policy
- After receiving the network access configuration command, enter the configuration (SoftAP/AirLink) mode and wait to receive SSID and password;
- If the SSID and password are successfully acquired, connect to the router automatically as specified in the connection policy;
- If successfully connected to the route, send the configuration success message (the module may restart);
- If the connection timeout happens in AirLink mode, it automatically enters SoftAP mode. When it times out in SoftAP mode, it is considered to be the configuration timeout.
- When obtaining the SSID/password times out, connect to the hotspot to which the Wi-Fi module most recently connected successfully as specified in the connection policy;
- If there is no hotspot in the cache, enter the unconnected mode (in STA mode and disconnected), which will not be entered again next startup.
7. Power-on policy
- After power-on, if there is no specified working mode, it will start in STA mode, and automatically connect to the router as specified in the previous policy;
- If there is no SSID information, enter SoftAP mode as specified in the previous policy.
8. Policy for reconnection to Gizwits IoT Cloud
- Reconnection to Gizwits IoT Cloud will be performed immediately after the device going offline.
- After first reconnection, the subsequent reconnection interval is increased by 10 seconds after each unsuccessful attempt, i.e., 10 seconds, 20 seconds, 30 seconds…
- When the reconnection attempts fail 10 times, re-acquire the device connection domain name from Gizwits IoT Cloud and perform DNS resolution after obtaining the domain name successfully.
- After the successful resolution, if the IP address changes compared to the previous one, immediately reconnect to the cloud, and the reconnection attempt interval starts from 0s and an incremental delay of 10 seconds is added to each reconnection attempt interval; If the IP address does not change compared to the previous one, continue reconnecting at the previous reconnection interval.
- When the reconnection attempt interval is increased to 10 minutes, it is no longer accumulated, and each reconnection attempt interval is kept at 10 minutes thereafter.
- If the reconnection attempt still fails after 1 hour, the device will restart (When it is not in Micro Cycle, restart after 2 minutes).
- If the connection to the router is unsuccessful, do not attempt to connect to Gizwits IoT Cloud.
- If connecting to the router successfully, connect to Gizwits IoT Cloud immediately, and the reconnection attempt interval starts from 0s and an incremental delay of 10 seconds is added to each reconnection attempt interval.
- If the connection to Gizwits IoT Cloud fails, follow the policy for the reconnection to Gizwits Cloud above.
Note: The device restart policy for disconnection to Gizwits IoT Cloud can be customized considering the Micro Cycle priority. If the priority of the Micro Cycle is high, the device will restart immediately when disconnected to Gizwits IoT Cloud. If the priority is medium, the device will restart only when there is no connection in Micro Cycle for consecutive 10 minutes. If the priority is low, the device can restart immediately when disconnected to Gizwits IoT Cloud.
9. Policy for reconnection to the router
- After disconnected to the router, the module enters the local mode (Micro Cycle and Macro Cycle are not available);
- After reconnected to the router successfully, the module enters the normal working mode (Micro Cycle and Macro Cycle are available), and restarts the Micro Cycle service and the Macro Cycle service;
- The module will restart after disconnected to the router and unable to establish the connection yet for more than 2 minutes.
10. OTA policy
GAgent OTA includes 4 steps: download, store, verify, and upgrade.
- Download: Get the download link and determine if it needs to download (the required hardware version matches and the new software version number is greater than the current software version number). Currently it does not support breakpoint transmission. It will not continue download after failure.
- Store: The file is being partitioned and saved into the flash cache area during download.
- Verify: Perform MD5 verification to confirm correct file transfer.
- Upgrade: There are two areas, master and backup. The program can still start normally from the other area in case of an upgrade failure.
MCU OTA includes 4 steps: download, store, verify, and transfer.
- The steps of download, store, and verify are the same as GAgent OTA;
- Transfer: Inform the MCU that there is firmware to be transferred. The firmware is transferred in slices and each slice needs to be verified using its checksum. After the transfer is completed, the MCU needs to perform MD5 verification. Then GAgent is restarted by the MCU to get the updated MCU information.
11. OTA push notification of Gizwits IoT Cloud
Gizwits IoT Cloud only notifies online devices of the OTA. For the devices that are not online at the time or have not upgraded successfully, the cloud will send OTA push notification once a day.
12. Basic requirement for GPRS module traffic
The data interaction between devices and Gizwits IoT Cloud mainly adopts MQTT protocol. The heartbeat data between the device and Gizwits IoT Cloud actually counts for a significant majority of the GRPS module traffic. The MQTT heartbeat consists of 2 bytes and the TCP protocol header size is 40 bytes. The heartbeat request and response happen once every 50 seconds. So the amount of data usage every 50 seconds is: (40 + 2) * 2 = 84 Bytes and the amount of monthly data usage is 4252K (calculated by 30 days a month). Therefore, the GPRS module needs at least 4252K data plan per month to ensure that it can access the Internet normally.
 Docs
Docs













